Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 irradiated with swift heavy ions
irradiated with swift heavy ionsKitamura, Akane; Ishikawa, Norito; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 44(3), p.85 - 88, 2019/06
Swift heavy ions can create nanosized hillocks on the surfaces of various ceramics. When these materials are irradiated with swift heavy ions at normal incidence, each ion impact results in the formation of a single hillock on the surfaces. In contrast, irradiation at grazing incidence forms chains of multiple hillocks on the surface, for example, for strontium titanate (SrTiO ). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO
). So far, chains of multiple hillocks have been investigated using atomic force microscopy (AFM). It should be noted that AFM measurements involve systematic errors of several nanometers due to the finite size of the probe tip. Consequently, it is possible that the image of one hillock may merge with that of a neighboring hillock even if the two hillocks are well separated. In contrast to AFM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) is a useful technique for obtaining higher-resolution images. In this study, we observed multiple nanohillocks on the surfaces of SrTiO using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO
using FE-SEM. Crystals of SrTiO (100) and 0.05 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO
(100) and 0.05 wt% Nb-doped SrTiO (100) were irradiated with 350 MeV Xe ions, respectively, at grazing incidence, where the angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2
(100) were irradiated with 350 MeV Xe ions, respectively, at grazing incidence, where the angle between the sample surface and the beam was less than 2 . On the SrTiO
. On the SrTiO surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO
surface, a chain of periodic nanohillocks is created along the ion path. In contrast, black lines accompanied by hillocks are observed on the Nb-doped SrTiO surface.
surface.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Harada, Makoto; Takano, Masahide
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 44(2), p.61 - 64, 2019/04
We performed three-dimensional observation of simulated fuel debris using Synchrotron Computed Tomography (CT). CT was used to make the inside of fuel debris clear. The CT observation provides that a clear contrast in the zirconia rich part and concrete rich part. Zirconia heavier than concrete moved to the lower part when crystals precipitate and aggregates near the bottom surface. As a result, phase separation occurs. The phase separation is caused by the difference in the composition ratio of zirconia, and can also be observed difference in crystal growth mode by composition ratio.
 In
In O
O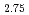 analyzed by neutron diffraction/ atomic pair distribution function
analyzed by neutron diffraction/ atomic pair distribution functionIgawa, Naoki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 43(6), p.329 - 332, 2018/12
For the understanding of the crystal structural effect on the electrical properties, the local disorder in BaSn In
In O
O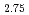 which is one of the excellent proton conductors for solid oxide fuel cells was estimated by using the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction. The local structure is almost the same as the average structure which was estimated by the Rietveld analysis using the cubic crystal structure (space group,
which is one of the excellent proton conductors for solid oxide fuel cells was estimated by using the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction. The local structure is almost the same as the average structure which was estimated by the Rietveld analysis using the cubic crystal structure (space group, 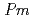
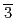
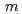 ) in the atomic distance range of
) in the atomic distance range of 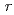
 6
6 . The PDF profile was fitted better using the tetragonal crystal structure with the space group of
. The PDF profile was fitted better using the tetragonal crystal structure with the space group of  4/
4/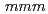 than those with
than those with 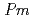
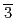
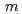 in the range
in the range 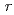
 6
6 . Those results indicate the presence of the local disorder in the lattice. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of BaSn
. Those results indicate the presence of the local disorder in the lattice. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of BaSn In
In O
O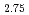 will be discussed.
will be discussed.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generators
Tc generatorsSuzuki, Yoshitaka; Kitagawa, Tomoya*; Namekawa, Yoji*; Matsukura, Minoru*; Nishikata, Kaori; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 43(2), p.75 - 80, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
 nanocrystals with cubic shape
nanocrystals with cubic shapeYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kunisada, Ryoichi*; Chikada, Tsukasa*; Ueno, Shintaro*; Ohara, Koji*; Wada, Satoshi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 43(2), p.93 - 96, 2018/04
KNbO nanocrystals were grown by solvothermal technique assisted by a microwave treatment. We performed high-energy X-ray diffraction to extract average and local structural parameters. The particle size can be evaluated by the Scherrer's equation. The unit cell size was reduced as the particle size increased. The local structure was found to be a rhombohedral structure, which was similar to that of the bulk KNbO
nanocrystals were grown by solvothermal technique assisted by a microwave treatment. We performed high-energy X-ray diffraction to extract average and local structural parameters. The particle size can be evaluated by the Scherrer's equation. The unit cell size was reduced as the particle size increased. The local structure was found to be a rhombohedral structure, which was similar to that of the bulk KNbO .
.
 Zy
Zy N surrogate materials for fast reactor nitride fuel
N surrogate materials for fast reactor nitride fuelYoneda, Yasuhiro; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Takaki, Seiya; Takano, Masahide
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 42(2), p.23 - 26, 2017/04
ZnN is a possible candidate for the diluent material for nitride fuels containing transuranium elements. Pellets of inert matrix material ZrN, and surrogate nitride fuel material Dy Zr
Zr N, are fabricated for the purpose of investigating the crystal structure. Lattice parameters of Dy
N, are fabricated for the purpose of investigating the crystal structure. Lattice parameters of Dy Zr
Zr N followed the Vegard's low, in spite of the large lattice mismatch (
N followed the Vegard's low, in spite of the large lattice mismatch ( 7%) between DyN and ZrN. Local structure analysis was performed by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) methods. The Zr-N nearest neighbor bond distance changed as changing the Dy composition. The complex local structure of DyN and ZrN is related to the preferable effects of ZrN.
7%) between DyN and ZrN. Local structure analysis was performed by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) methods. The Zr-N nearest neighbor bond distance changed as changing the Dy composition. The complex local structure of DyN and ZrN is related to the preferable effects of ZrN.
Mayumi, Ren*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Saito, Yuichi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 42(1), p.9 - 14, 2017/02
AlCu binary alloys were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni or 4.5 MeV Al ions at room temperature. Changes in surface hardness and the local atomic structure around Cu atoms were examined by using the Vickers hardness measurement and the EXAFS measurements, respectively. Some specimens were aged at 453 K and Vickers hardness was measured. The computer simulation was also performed by using the rate equation method. The hardness of irradiated specimens increased much faster than that of the aged specimens and it became larger than the maximum value of the hardness for the aged specimens. The comparison of the experimental EXAFS result with that of FEFF simulation suggests that the ion irradiation produced small Cu precipitates in the specimens. The computer simulation visualized the growth process of Cu precipitates during the irradiation, and the result qualitatively corresponds to the experimental result.
 K
K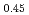 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO solid solutions by malic acid complex solution method
solid solutions by malic acid complex solution methodNakai, Tomoaki*; Kobune, Masafumi*; Nagamoto, Takeru*; Kikuchi, Takeyuki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 41(3), p.251 - 254, 2016/09
Solid solutions of NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO are the candidate for non-Pb piezoelectric materials. It is difficult to obtain dense ceramics owing to the difference of their calcination temperature. We developed the malic acid complex method to obtain the (Na
are the candidate for non-Pb piezoelectric materials. It is difficult to obtain dense ceramics owing to the difference of their calcination temperature. We developed the malic acid complex method to obtain the (Na K
K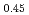 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO to obtain a high-quality ceramics sample. It was found that (Na
to obtain a high-quality ceramics sample. It was found that (Na K
K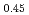 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO lies complicated phase boundaries; one is the structural phase boundary between NaNbO
lies complicated phase boundaries; one is the structural phase boundary between NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO , the other is that between (Na,K)NbO
, the other is that between (Na,K)NbO mixture and LiNbO
mixture and LiNbO , which is a sintering additive.
, which is a sintering additive.
 Na
Na TiO
TiO , Bi
, Bi Na
Na Li
Li TiO
TiO , and 0.95Bi
, and 0.95Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO
 0.05BaMn
0.05BaMn V
V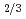 O
O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Nagamoto, Takeru*; Nakai, Tomoaki*; Kobune, Masafumi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 41(2), p.197 - 200, 2016/06
Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO (BNT) has been investigated as a lead-free piezoelectric material. We have already performed structure analysis of BNT. The average structure of BNT with low-temperature synthesis is a rhombohedral structure and it becomes a monoclinic structure as the synthesized temperature increases. Our local structure analysis indicated that the
(BNT) has been investigated as a lead-free piezoelectric material. We have already performed structure analysis of BNT. The average structure of BNT with low-temperature synthesis is a rhombohedral structure and it becomes a monoclinic structure as the synthesized temperature increases. Our local structure analysis indicated that the 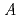 -site atoms of Bi and Na displaced toward different position depending on the lattice expansion and construction. We synthesized BNT crystals with various substitution and performed local structure analysis to examine the hypothesis. The local structure analysis revealed that the substitution effect on BNT can be explained by our hypothesis.
-site atoms of Bi and Na displaced toward different position depending on the lattice expansion and construction. We synthesized BNT crystals with various substitution and performed local structure analysis to examine the hypothesis. The local structure analysis revealed that the substitution effect on BNT can be explained by our hypothesis.
 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
 modulated by Mn substitution
modulated by Mn substitutionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Noguchi, Yuji*; Miyayama, Masaru*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(1), p.29 - 32, 2015/03
Barium titanate (BaTiO ) with a high dielectric constant is widely used in the production of ceramic capacitors. However, during sintering large numbers of ionized oxygen vacancies and conduction electrons are created. Doping with manganese is one of several ways to confine the electrons to a small region. In Mn-doped BaTiO
) with a high dielectric constant is widely used in the production of ceramic capacitors. However, during sintering large numbers of ionized oxygen vacancies and conduction electrons are created. Doping with manganese is one of several ways to confine the electrons to a small region. In Mn-doped BaTiO there exist three valence states for the manganese ions, Mn
there exist three valence states for the manganese ions, Mn , Mn
, Mn , and Mn
, and Mn . The Mn
. The Mn is nearly exactly incorporated into Ti
is nearly exactly incorporated into Ti sites and participates in the collective motion in the lattice. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). Figure 1 shows the obtained PDFs for pure BaTiO
sites and participates in the collective motion in the lattice. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). Figure 1 shows the obtained PDFs for pure BaTiO and 0.5%-Mn-doped BaTiO
and 0.5%-Mn-doped BaTiO . All data collected at room temperature. Two obtained PDF patterns are well in agreement. Mn doping has hardly affected local structure.
. All data collected at room temperature. Two obtained PDF patterns are well in agreement. Mn doping has hardly affected local structure.
 molecules"
molecules"Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(1), P. 85, 2015/03
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Nagata, Hajime*; Fu, D.*; Takenaka, Tadashi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 39(4), p.455 - 458, 2014/12
NaNbO , KNbO
, KNbO , and AgNbO
, and AgNbO have rhombohedral structure at low temperatures. The phase transition depends on
have rhombohedral structure at low temperatures. The phase transition depends on 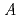 -site ion with NbO
-site ion with NbO octahedron. NaNbO
octahedron. NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO have structural phase transition from rhombohedral to orthorhombic with increasing temperature. On the other hand, the phase transition of AgNbO
have structural phase transition from rhombohedral to orthorhombic with increasing temperature. On the other hand, the phase transition of AgNbO occurs from rhombohedral to monoclinic. Since the rhombohedral structure is a highly ordered average structure, it tends to be subject to the influence of local randomness. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF). The Nb-O bond clearly appeared in the observed distribution for NaNbO
occurs from rhombohedral to monoclinic. Since the rhombohedral structure is a highly ordered average structure, it tends to be subject to the influence of local randomness. We performed local structure analysis by using atomic pair-distribution function (PDF). The Nb-O bond clearly appeared in the observed distribution for NaNbO , but degraded in that for AgNbO
, but degraded in that for AgNbO . The difference of local structures causes different successive phase transitions for the Nb-related perovskite materials.
. The difference of local structures causes different successive phase transitions for the Nb-related perovskite materials.
 Na
Na )TiO
)TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Aoyagi, Rintaro*; Fu, D.*; Takenaka, Tadashi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 39(3), p.247 - 250, 2014/09
Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO are
are 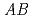 O
O perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi
perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.
to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.
Ito, Fuyumi; Nishimura, Akihiko
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(4), p.667 - 672, 2013/12
We are proposing Magnetic particle Testing (MT) using fabricated micro capsules by the hand-shake method. Here a test piece magnetized beforehand is immersed in liquid dispersed with magnetic particles. Fluorescent pigment adheres to the magnetic particles. So, MT is able to facilitate the crack visually as long as a certain amount of magnetic particles are holding the fluorescent pigment. However, separation between particle and pigment degrades transparency in liquid. Finally the hazy liquid makes difficult to find any crack. To solve this problem, we propose to use the Magnetic Particle Micro Capsule (MPMC). In addition, to applying this MPMC, the surround of the nuclear power plant should be confirmed. To confirm inside wall, the Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied.
 MnO
MnO (
(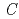 2/
2/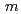 ) for a lithium-battery cathode in several charge-discharge potential ranges
) for a lithium-battery cathode in several charge-discharge potential rangesNakao, Yasuhiro*; Ozawa, Kiyoshi*; Fujii, Hiroki*; Mochiku, Takashi*; Iwai, Hideo*; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Igawa, Naoki
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(2), p.229 - 233, 2013/12
Li MnO
MnO powder with a monoclinic cell related to the space group of
powder with a monoclinic cell related to the space group of 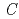 2/
2/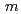 was synthesized by a simplified coprecipitation method. Its electrode properties as a lithium-battery cathode were investigated in the charge-discharge potential ranges of 2.0 - 4.6, 2.0 - 4.8, and 2.0 - 5.0 V. In all the potential ranges, the electrochemical capacities gradually increased during cycling, and the increased capacities significantly depended on the potential ranges. Compared to the discharge capacities for the potential ranges of 2.0 - 4.6 and 2.0 - 5.0 V, the former merely increased from 12.5 to 22.5 mAhg
was synthesized by a simplified coprecipitation method. Its electrode properties as a lithium-battery cathode were investigated in the charge-discharge potential ranges of 2.0 - 4.6, 2.0 - 4.8, and 2.0 - 5.0 V. In all the potential ranges, the electrochemical capacities gradually increased during cycling, and the increased capacities significantly depended on the potential ranges. Compared to the discharge capacities for the potential ranges of 2.0 - 4.6 and 2.0 - 5.0 V, the former merely increased from 12.5 to 22.5 mAhg between the 1st and 99th cycles, whereas the latter increased from 20.0 to 110.2 mAhg
between the 1st and 99th cycles, whereas the latter increased from 20.0 to 110.2 mAhg during the same cycling. The structural variation in Li
during the same cycling. The structural variation in Li MnO
MnO is induced by the cycling, the rhombohedral phase is detected during cycling in the potential range of 2.0 - 5.0 V.
is induced by the cycling, the rhombohedral phase is detected during cycling in the potential range of 2.0 - 5.0 V.
Kada, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Akihito; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(3), p.443 - 446, 2013/09
Microscopic imaging and analysis techniques are increasing its importance and being interested from the environmental research fields especially for the target with a complex elemental or chemical structures. Electron or synchrotron-radiation microbeam probes are quite poplar scanning analytical probing techniques for the imaging of such microscopic targets. On the other hand, microbeam techniques using MeV ions have also utilized for such analysis purpose with advantages in the aspect of sensitivity and S/N ratios. However, these Ion Beam Analysis (IBA) techniques like PIXE (Particle Induced X-ray Emission) do not have enough sensitivity in the chemical-state analysis. This limits the application area of IBA techniques compared to the other beam probes. In this study, an new ion microbeam technique with Microscopic by spectroscopic analysis of IL was developed and combined with micro-PIXE system for the simultaneous analysis and imaging of chemical-state distribution in microscopic targets. Spectroscopy of IL from the National Institute of Environmental Science (NIES) aerosol standards was first achieved to visualize chemical state distribution in such microscopic analytical targets with spatial resolution of 1 m.
m.
Kada, Wataru; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Iwamoto, Naoya; Onoda, Shinobu; Grilj, V.*; Skukan, N.*; Makino, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Sato, Takahiro; Jak i
i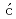 , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(2), p.279 - 282, 2013/07
Diamond is interested by many researchers as an excellent candidate material with advantages in the radiation-hardness. For the time-resolved detection of single-ions with several hundred MeV, transmission E detector using thin film CVD diamond is now under investigation for the futuristic utilization in a microbeam line of the AVF cyclotron at JAEA/Takasaki TIARA facility as replacing materials of the beam extraction window. In this research, a Single Crystalline (SC) 50 m thick CVD diamond film ion detector was fabricated for the investigation of the responses and radiation hardness under the focused ion microbeam irradiation. Transient Ion Beam Induced Current (TIBIC) experiment was executed by single hit irradiation of 15 MeV O scanning area of 50
scanning area of 50  m
m and the transient signals with time width of several nano-secounds were consecutively recorded by a high speed (15 GHz) Digital Storage Oscilloscope during the irradiation. The decreases in the individual pulse height was observed by increasing the total amount of the ion dose irradiated in the focused area. These changes were recovered in temporal conversion of applied bias voltages thus trend of decrease were able to be controlled by changing bias settings and irradiation conditions during the experiments.
and the transient signals with time width of several nano-secounds were consecutively recorded by a high speed (15 GHz) Digital Storage Oscilloscope during the irradiation. The decreases in the individual pulse height was observed by increasing the total amount of the ion dose irradiated in the focused area. These changes were recovered in temporal conversion of applied bias voltages thus trend of decrease were able to be controlled by changing bias settings and irradiation conditions during the experiments.
Kitamura, Akane; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.101 - 104, 2013/03
Hamamoto, Satoshi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Hojo, Kiichi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.89 - 92, 2013/03